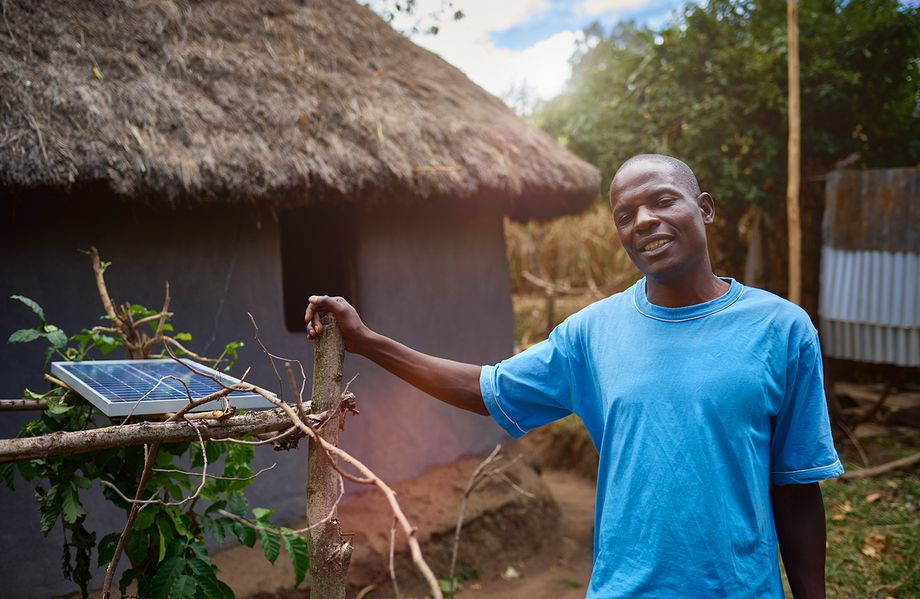
Energy demand in Africa is enormous. The need of people for electricity to read, to inform themselves or even to earn a small income thanks to electricity is immense. Currently more than 620 million Africans do not have access to electricity and this number will even increase by 45 million in 2030. Grid extensions are expensive, complex and slow to implement. In contrast off-grid household power solutions provide an affordable option to rural households in Africa. It is expected that 70% of rural households will gain access to electricity through off-grid solutions.
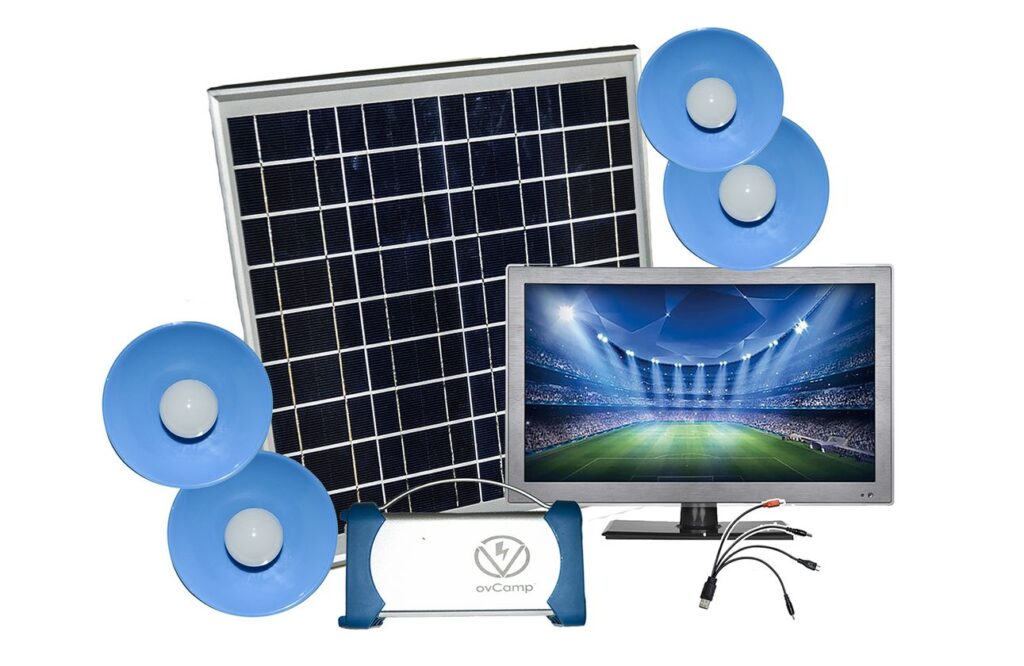
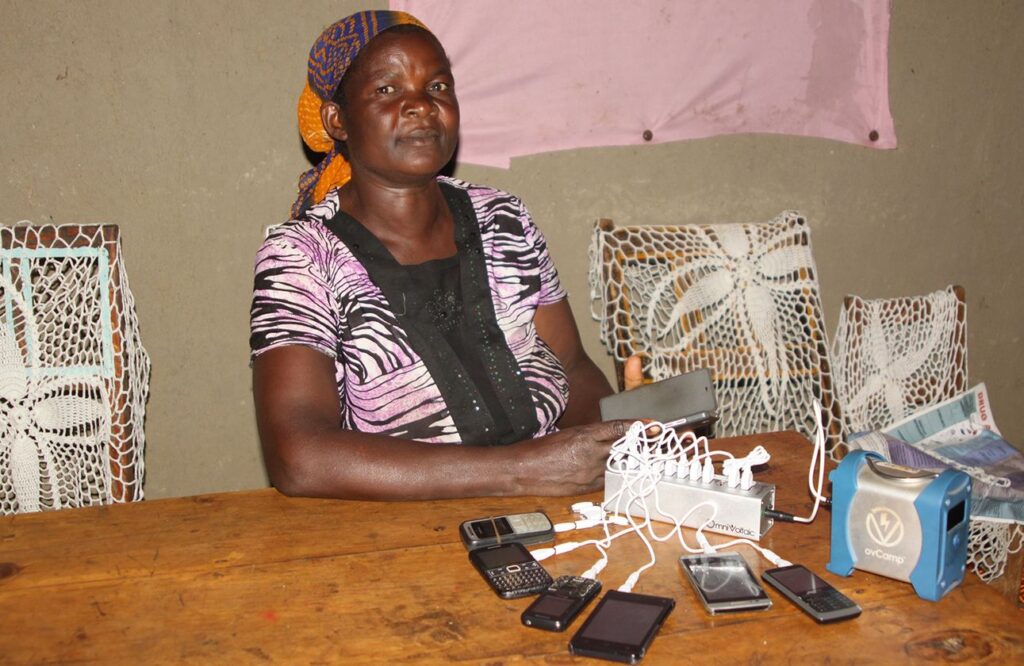
The mission of this project is to bring affordable, flexible electricity to a consistently under-served population. The project offers modular so called solar home systems of various sizes coupled with usable appliances such as lights, TV, radio, or phone charging stations to households, schools, churches and business in rural Kenya.
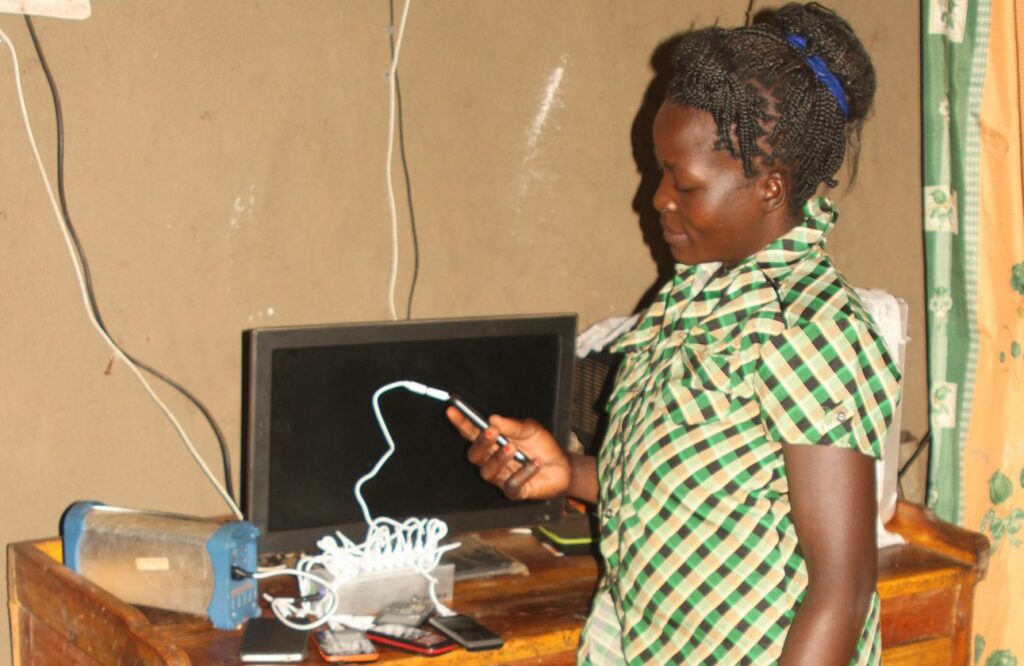
The light bulbs have never gone out since I got the solar kit, and thanks to my television I can keep myself politically informed and was able to make a self-determined choice in the last presidential elections. My family is in better health since we no longer need kerosene lamps.
Jentrix Khabakali, owner of a solar kit
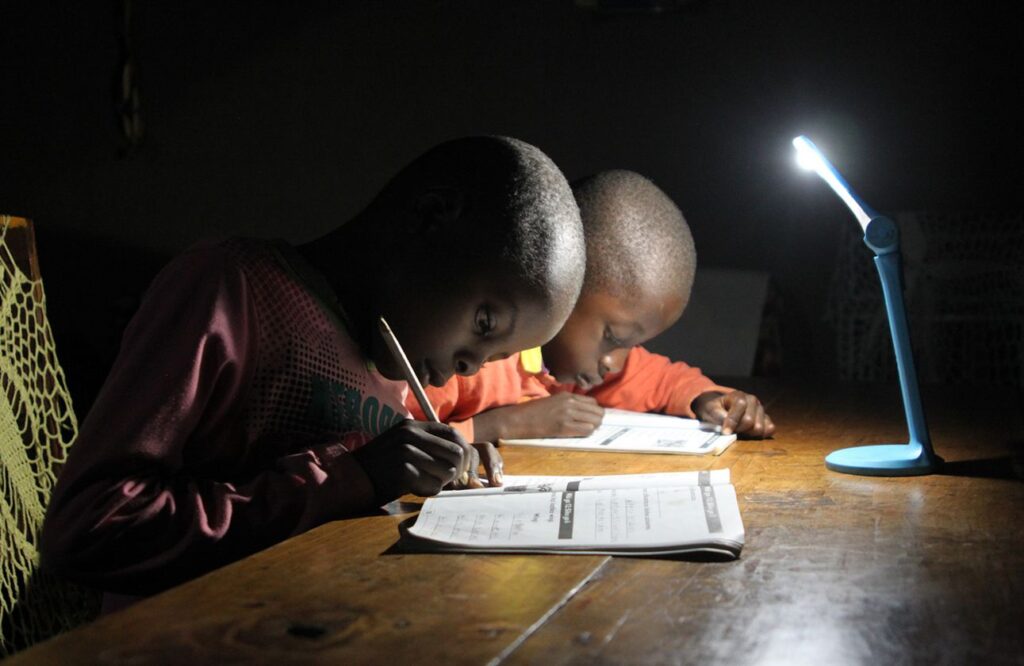
Introducing solar power to underserved communities in rural areas in Kenya shows many benefits such as reducing CO₂ emissions and kerosene consumption, increasing study and working time (in Kenya the sun sets at 6pm all year round), giving access to information and news through radio and TV and providing power to start small businesses such as phone charging or barber shops fostering economic development. In addition, people no longer suffer from power cuts, feel safer and are better able to protect their livestock against theft at night.
One main obstacle to acquire solar power is lack of capital. Solibrium, the project partner of myclimate in Kenya, aims to make off-grid solar power affordable and thus offers its clients flexible and variable payments plans of up to two years. This requires considerable funds for pre-financing the solar home systems.
The motto of myclimates project partner Solibrium is “Nuru Maishani”. This is Swahili and means “Light in your life”.
myclimate supports Solibrium with capital for ordering solar kits, for training of rural sales people and for growing the countrywide sales and repair network. Capital for pre-financing is managed in a revolving fund and allows Solibrium to scale its activities by ordering additional kits once income from sales has materialized.
myclimate is not only supporting the dissemination of solar power in Kenya, but also works on solutions to what happens once solar products have reached end-of-life. With the emergence of pay-as-you-go models, more and more families can afford solar home systems providing power for multiple lights and to small appliances such as phones, radios, televisions, and refrigerators. With the millions of off-grid solar products being distributed annually, millions of batteries and other electronic equipment are also brought out to remote areas. Kenya has some legislation for recycling of batteries, but the legislation is not enforced in rural areas. Batteries and other electronic parts, when dumped in rivers, lakes, on agricultural land or when burnt, may cause severe environmental pollution and pose health risks.
Amongst consumers and society there is limited knowledge and very low level of awareness about the hazards of not appropriately recycled batteries and electronic equipment.
Further, e-waste centres are not common in Africa and if they exist they are located in cities, whereas most users of off-grid solar products are located in rural areas. Thus, there is the need for solutions for e-waste management that are accessible and understandable to rural off-grid solar product users.
myclimate and Solibrium are working on solutions for e-waste from off-grid solar products in a co-funded project in Western Kenya with grant money from the Swiss federal government (repic) and the Gobal LEAP Awards addressing the specific challenges in rural areas. This project aims at creating awareness among stakeholders for the problem of e-waste from off-grid solar products and for possible solutions. Further, the project will define and test measures to extend the life of solar products (especially the battery) to ensure that they enter the waste cycle as late as possible. And the project will develop and test business models for take-back schemes, reuse, and/or recycling or safe disposal of off-grid solar products to provide economic viable solutions for e-waste management. Best practices and business models are selected and assessed based on their economic viability and on their environmental impact.

Justcote Ltd.
Company number: 13881985
Address: Devonshire House, Ettingshall Rd, Wolverhampton WV2 2JT
Telephone: +44 333 050 3479
![]()